COVID-19 检测专家指南
一名流行病学家讨论了分子检测和快速检测之间的区别、其准确性以及人们应何时接受冠状病毒检测。

随着具有高传染性的奥密克戎变异病毒在美国传播,检测是帮助控制 COVID-19 传播的关键工具之一。NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center 的首席医院流行病学家 David Calfee 医生表示,“检测是全球疫情控制工作的的几个重要部分之一”。“它使得有症状的 COVID-19 患者能够接受适当的护理和治疗,并有助于减少 SARS-CoV-2 病毒从有症状、无症状或症状前感染患者处传播。”
但是随着越多越多的人寻求检测,疑问仍然存在,包括检测类型之间的差异、COVID 结果的准确性以及人们何时需要接受检测。
Calfee 医生也是 Weill Cornell Medicine 的医学教授兼 NewYork-Presbyterian 的感染预防控制科的副医务主任,他接受了 Health Matters 的采访,并回答了这些问题。

Dr. David Calfee
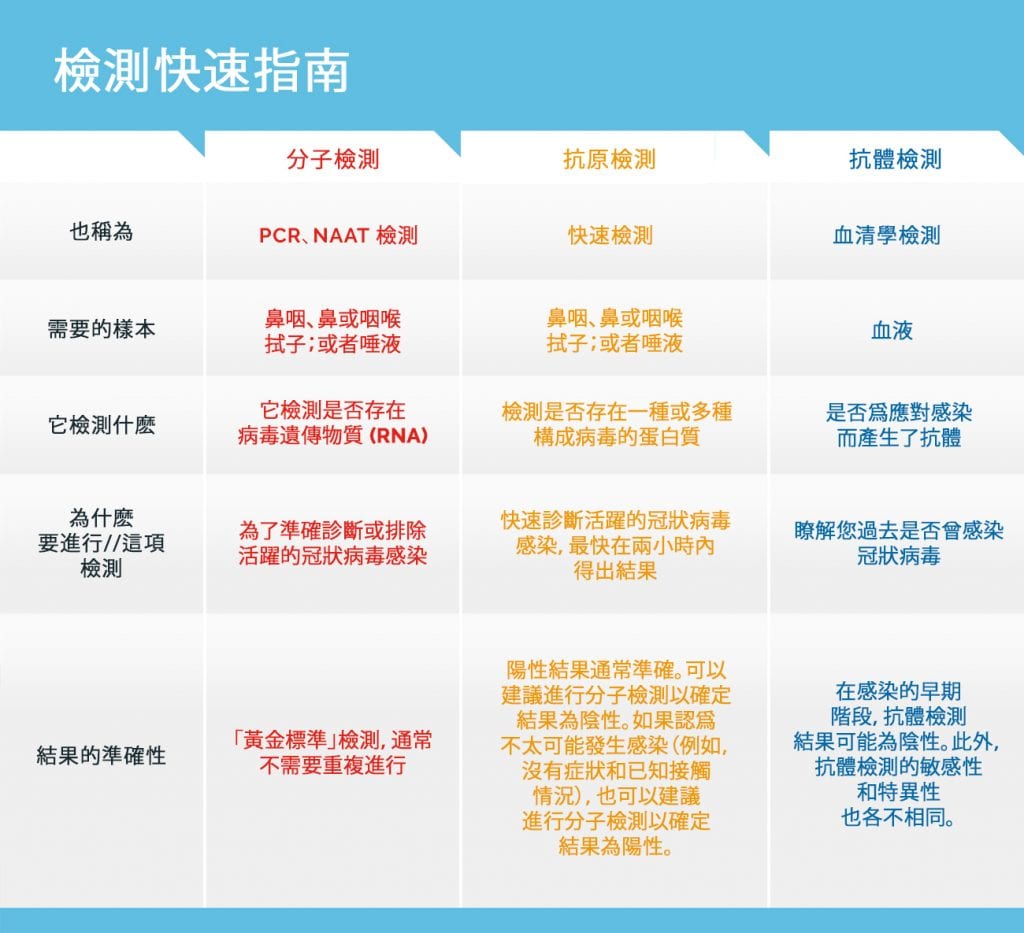
什么是 PCR 检测?
聚合酶链反应 (PCR) 和核酸扩增检测 (NAAT) 是分子检测。分子检测可检测出病毒遗传物质(即核糖核酸)的存在。一般而言,这些检测被视为 COVID-19 诊断的“黄金标准”。它们的敏感性比抗原检测更高,这意味着它们可以检测出更多 COVID-19 感染者。PCR 检测通常需要 24 小时才能出结果,但如果对化验进行备份,则需要更长时间。
什么是抗原检测?
抗原检测(也称为快速检测)可检测出病毒中的一种或多种蛋白质的存在。抗原检测可以快速出结果,因为它们需要的技术不太复杂。它们通常比分子检测周期更快,您可以很快从医生诊所或紧急护理机构处获得结果。居家抗原检测也可以在药店和线上购买,其中一些已经获得 Food and Drug Administration(食品药品监督管理局)在紧急使用授权下的批准。快速居家检测是现有的优秀工具,尤其是在很难找到 PCR 检测且出现症状的情况下。
抗原检测的假阳性结果很少,但由于抗原检测的敏感性较低,因此可能出现假阴性结果。这一点很重要,因为抗原检测结果呈阴性并不一定意味着您未感染病毒。如果您有 COVID-19 症状或有理由怀疑您已接触病毒,例如与后来 COVID-19 检测结果呈阳性的人员密切接触,建议您用利用 PCR 检测对阴性的抗原检测结果进行确认。此外,请务必注意,在接触 COVID-19 患者后立即检测出的阴性结果(抗原或 PCR 检测)并不能证明您未感染,因为病毒可能需要过几天才能检测出来。
人们应何时接受检测?
尽管地方和州卫生部门以及其他机构和雇主的具体建议各不相同,但优先接受检测的群体均是有 COVID-19 症状的人员,以及已知接触 COVID-19 的人员。建议进行检测的其他情况包括出行和参加大型聚会前后、开刀的医疗程序和手术之前、以及在长期护理机构或其他集中居住环境中工作或生活的人员。
到校上课的儿童是否应定期接受检测?
各个地区的要求可能有所不同。但是,无论学校的检测要求是什么,务必要遵守预防和缓解策略,例如疫苗接种(如果符合资格),以及使用面罩、保持社交距离和手部卫生。
根据 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(疾病控制和预防中心)的最新指南,COVID-19 检测结果呈阳性的人员可以在 5 天后停止隔离(如果无症状),并在随后的 5 天里与其他人接触时要佩戴口罩。为什么呢?
此建议所依据的数据表明,大多数 COVID-19 患者的传染性下降非常快。他们发现,大多数 SARS-CoV-2 传播发生在患病初期,即出现症状前 1 至 2 天和出现症状后 2 至 3 天。即使患者不再具有传染性,分子检测结果也依然会呈阳性,因为这些检测能够检测出非常少量的病毒遗传物质。但是,对于病情更严重的 COVID-19 患者以及免疫系统严重受损的个人,建议实施更长时间的隔离。
David P. Calfee(医学博士,理科硕士)是 New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center 的首席医院流行病学家兼 NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital 的感染预防控制科的副医务主任。他也是 Weill Cornell Medicine 的医学(传染病)和人口健康科学教授。Calfee 医生是 Infectious Diseases Society of America 和 Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America 的研究员,也是 Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 的编辑。他的研究领域包括抗菌药物耐药性病原体、流行病学和医疗护理相关感染的预防。

