Can Collagen Supplements Really Reduce Signs of Aging?
Dermatologist Dr. Shari Lipner breaks down the popular health trend that claims to improve skin elasticity and overall appearance.


Coconut oil, step aside. There’s a new health craze in town: collagen supplements.
It’s a trend that’s growing — most notably for its claims of improving skin’s elasticity and promoting a vibrant, youthful complexion. Collagen supplements are believed to have other health benefits, including strengthening bones, promoting hair growth, and improving joint health.
Collagen is one of the major building blocks of bones, skin, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The word collagen comes from the Greek word kolla, which means glue. It’s no wonder, then, that collagen has been used for decades as an injectable filler to plump lips and soften wrinkles. In recent years, it has become more and more accessible, with pill and powder forms readily available. A “collagen booster” is even an option at some smoothie counters.
To learn more, Health Matters consulted with Dr. Shari Lipner, a dermatologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, on what collagen is, how it works, and whether it truly is the “fountain of youth” people hope it to be.
What is collagen and why is it important for our bodies?
Collagen is a fibrous, supportive protein. It is found in bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and skin. It helps skin cells adhere to one another and also gives the skin strength and elasticity. Collagen production decreases with age, contributing to skin wrinkling and sagging.
What are some other health benefits of collagen?
There is some evidence that collagen supplements improve joint pain and osteoarthritis.
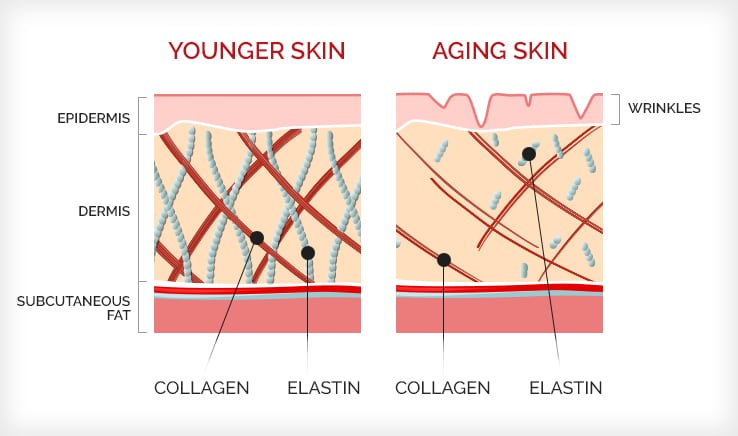
As we get older, skin shows signs of aging due to reduced collagen and elastin production as well as other factors such as exposure to UV rays and tobacco.
What are the different forms of collagen supplements, and is one form better than another?
Collagen supplements are synthesized into protein chains called collagen hydrolysates and are absorbed by the body and then used directly by skin cells. They come in pill and powder forms. The powders should be dissolved in hot or cold liquid prior to consumption. There are no studies that compare the different collagen products, so we do not know if one supplement is better than another.
There’s a lot of hype around taking collagen supplements for younger-looking skin. Can they really slow the skin’s aging process?
There are some small studies showing improved skin elasticity and appearance of the skin after taking collagen hydrolysate supplements for at least six weeks. Keep in mind that we do not know if these effects are long-lasting and that there was no control group in some of the studies.
Are there any ingredients or things to look out for when buying collagen supplements?
Key words to look for in the ingredients are collagen hydrolysate, hydrolyzed collagen, or collagen peptides.
So, should we believe the hype?
There are some small studies showing that collagen improves skin elasticity. However, these studies were small and uncontrolled. Right now, we do not have good evidence that there is benefit to taking collagen supplements. I would advise my patients to avoid taking these supplements until we have more convincing data of benefits and until we can be sure of safety.
Any idea how long that will be?
We need to see data from randomized, controlled studies to really understand the effect of oral collagen on skin aging. This means we have to compare a group of people taking collagen supplements to a group not taking the supplement. There is currently one such study enrolling patients, so it should not be long before we can make recommendations to our patients.
Are there certain foods or drinks that contain collagen?
Red meats, chicken, fish, nuts, beans, and grains contain adequate quantities of collagen.

Dr. Shari Lipner
Does eating food with collagen help improve the elasticity of your skin?
The collagen in food cannot be used directly by our tissues. It is a long chain of amino acids that must be first broken down by enzymes into a shorter, more usable form. Collagen supplements have already gone through this enzymatic process of hydrolysis into shorter amino acid chains.
Are there any cons to taking collagen supplements?
So far, the only known side effect of collagen supplements is stomach upset. However, we may find out others if this trend increases in popularity or from larger studies.
Given that there is not enough evidence to prove that collagen supplements can reduce signs of aging, is there anything that you recommend to improve the skin’s elasticity and/or reduce signs of aging?
The best ways to prevent signs of skin aging are to use sun protection, eat a well-balanced diet, and avoid smoking. A board-certified dermatologist can prescribe a retinoid cream and/or perform noninvasive procedures to reduce signs of skin aging.
Shari Lipner, M.D., Ph.D., is a board-certified dermatologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center and an assistant professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine. She treats patients with common dermatologic problems of skin, skin cancers, and cosmetic concerns, as well as nail conditions. She has authored more than 70 manuscripts and book chapters on skin conditions and cosmetics, lectures nationwide, and is frequently called upon by the media for her expert opinion.

